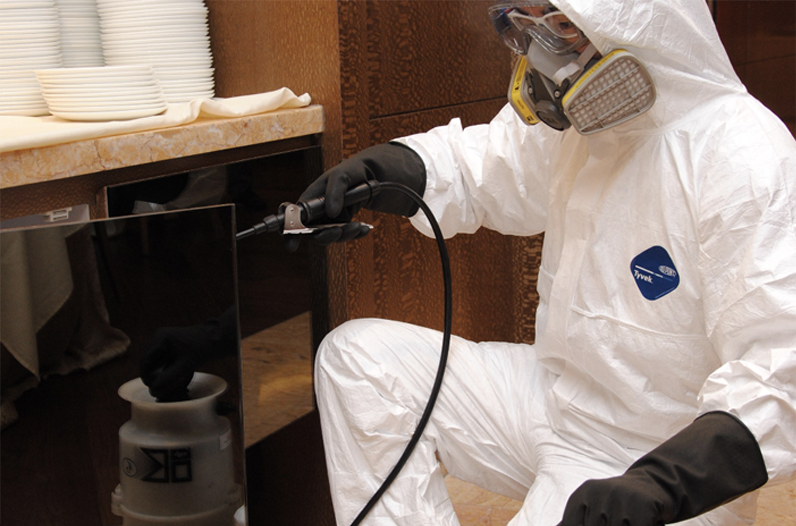
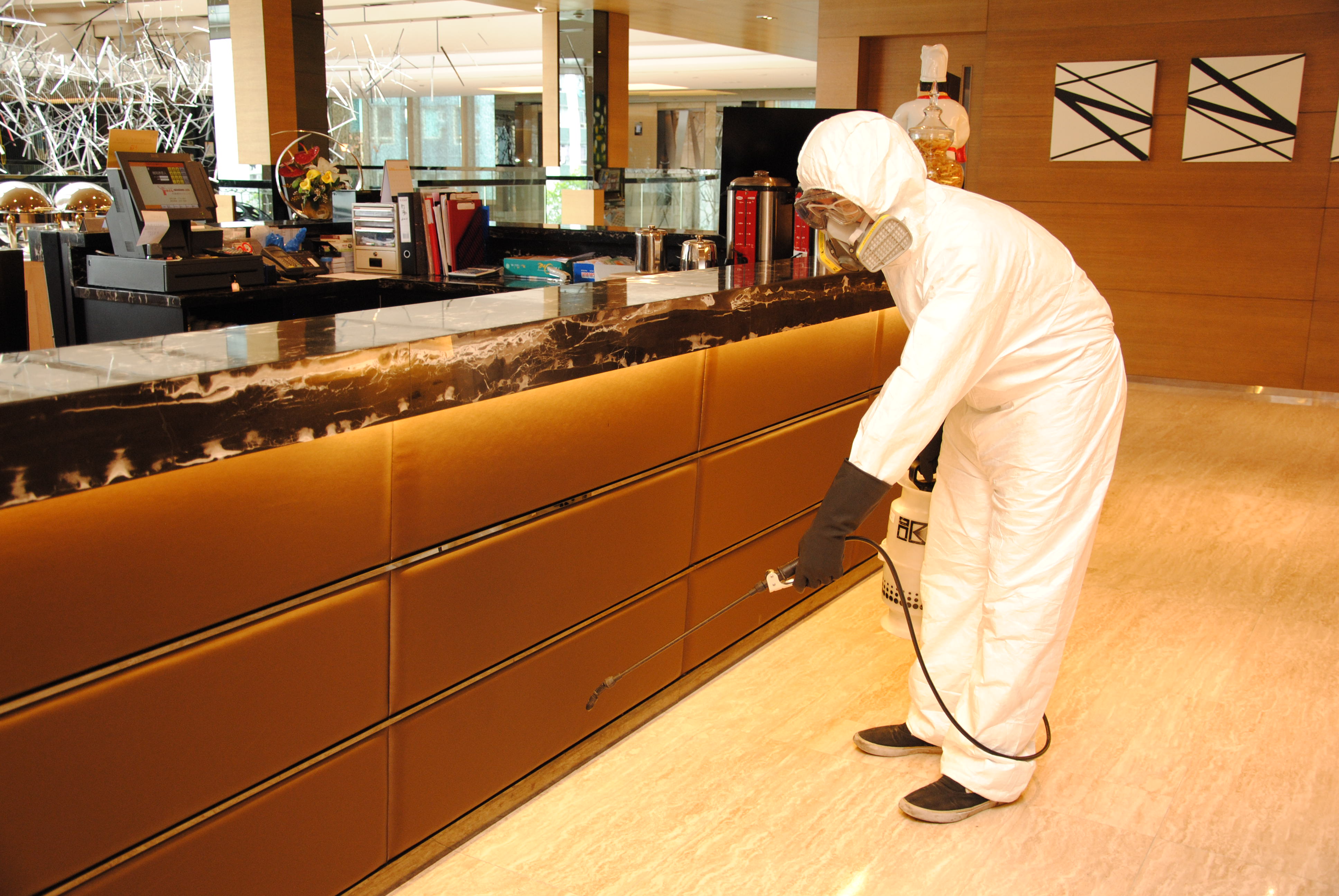
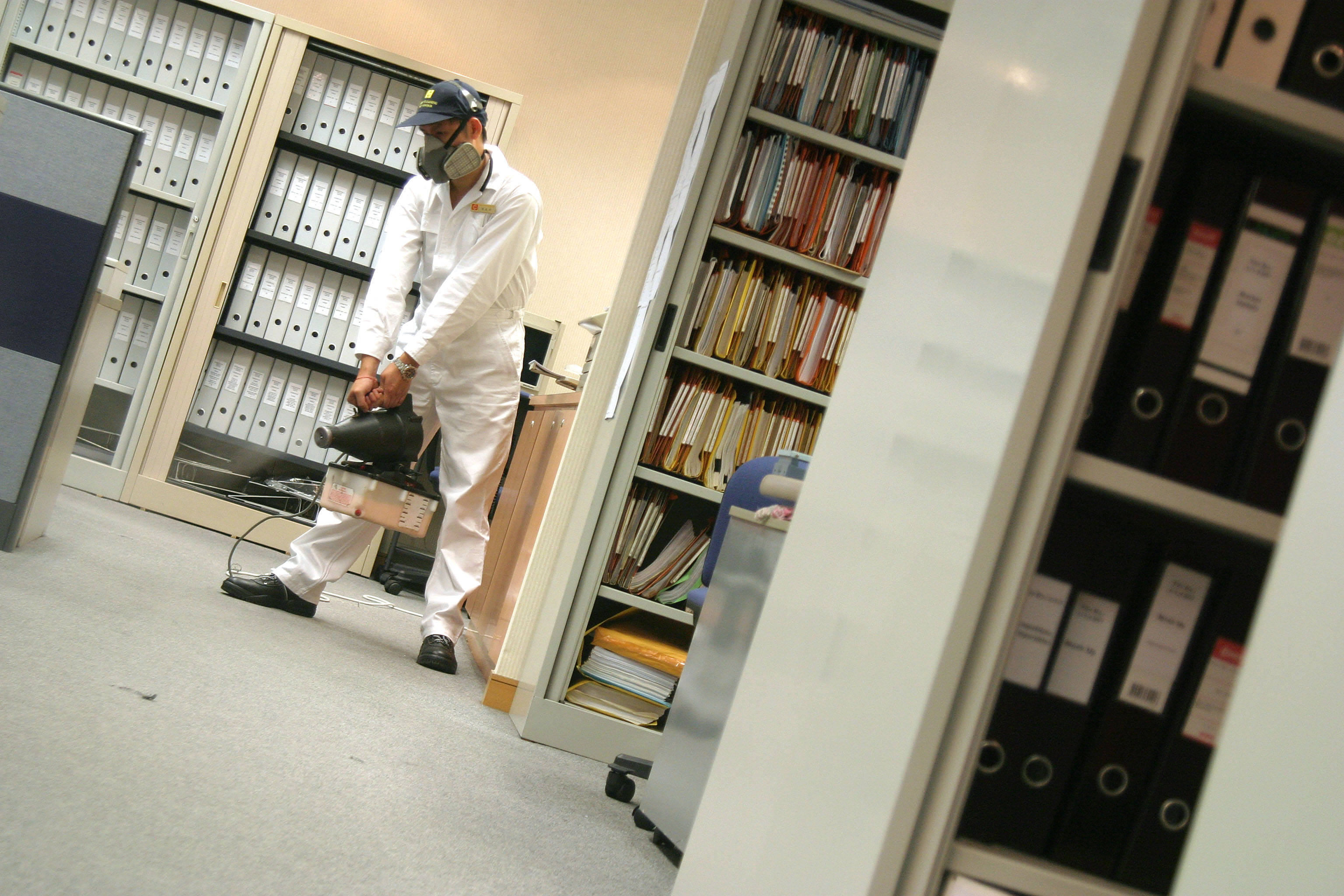
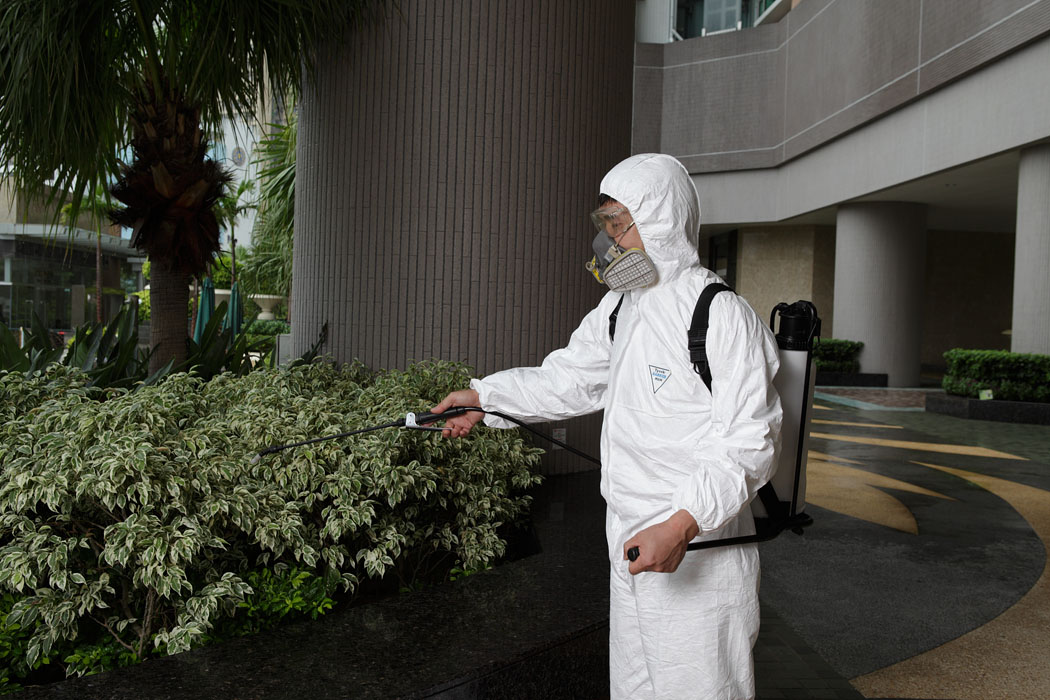
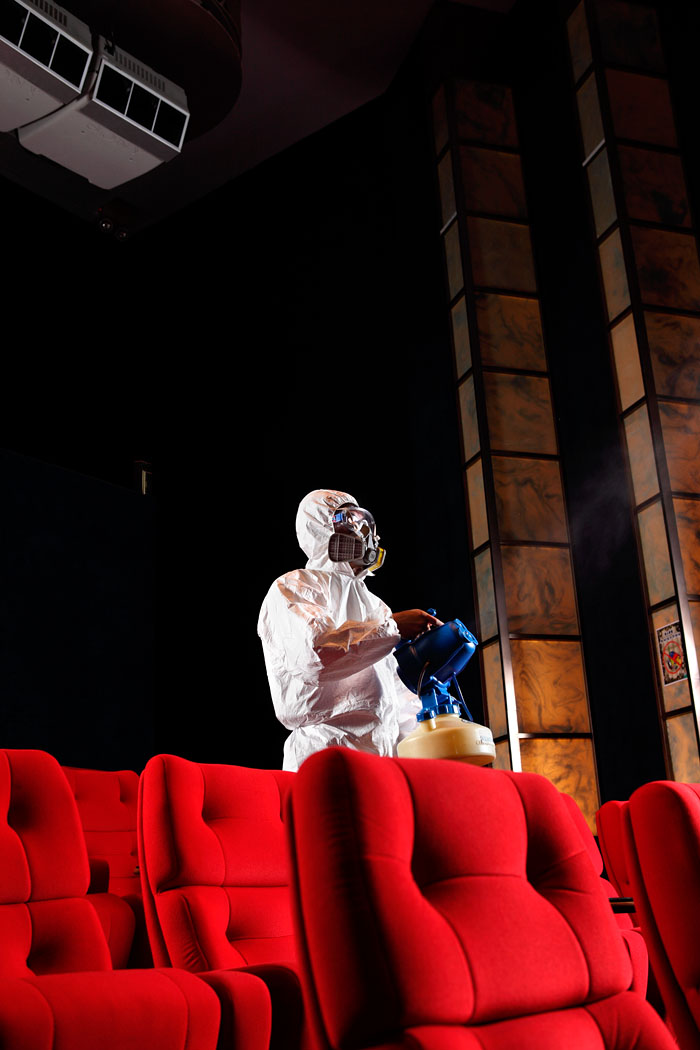
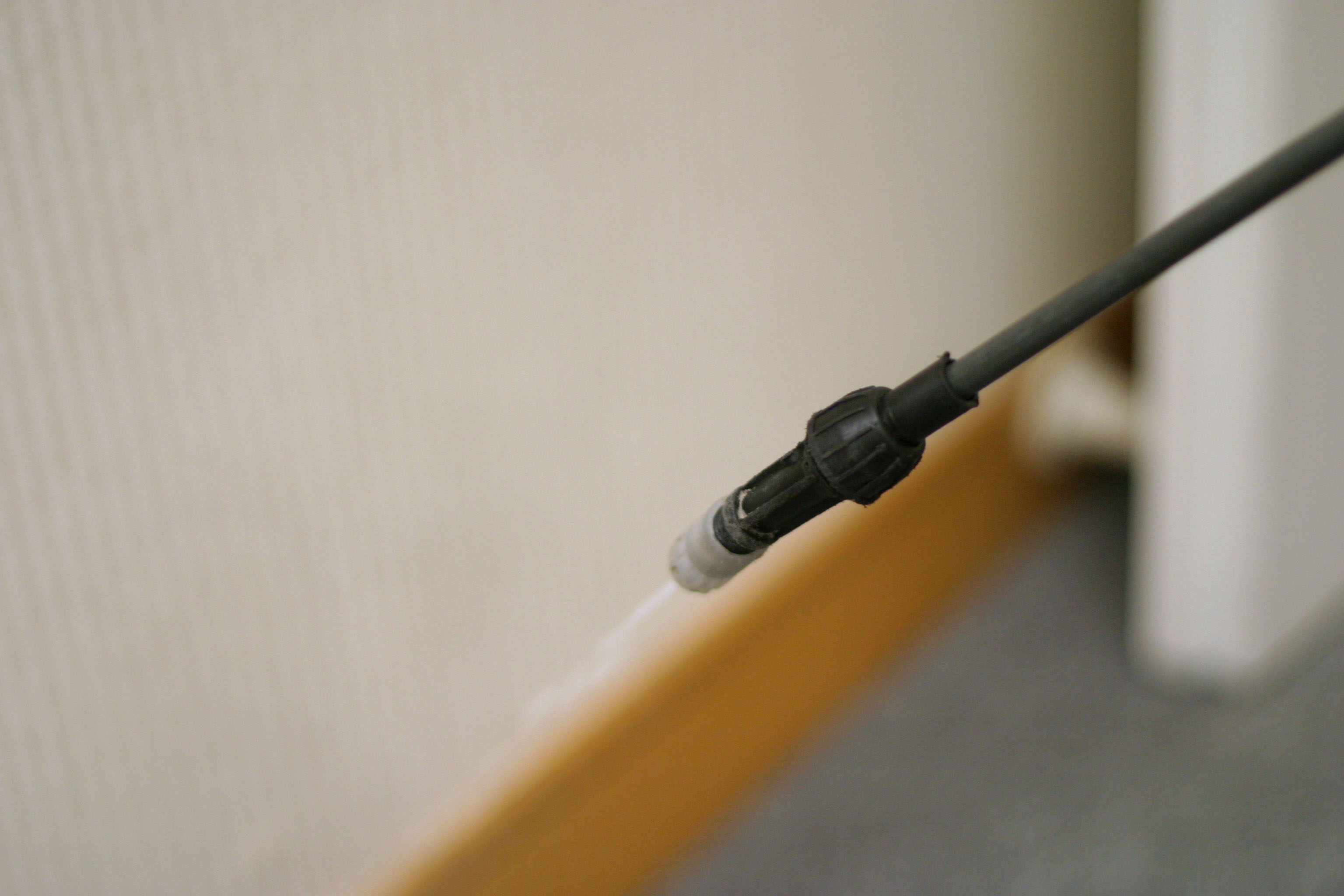
Residential & Commercial Pest Control Services
- Termites
- Cockroaches
- Fleas
- Bees
- Mosquitoes
- Ants
- Rodents
- Other Common Insects
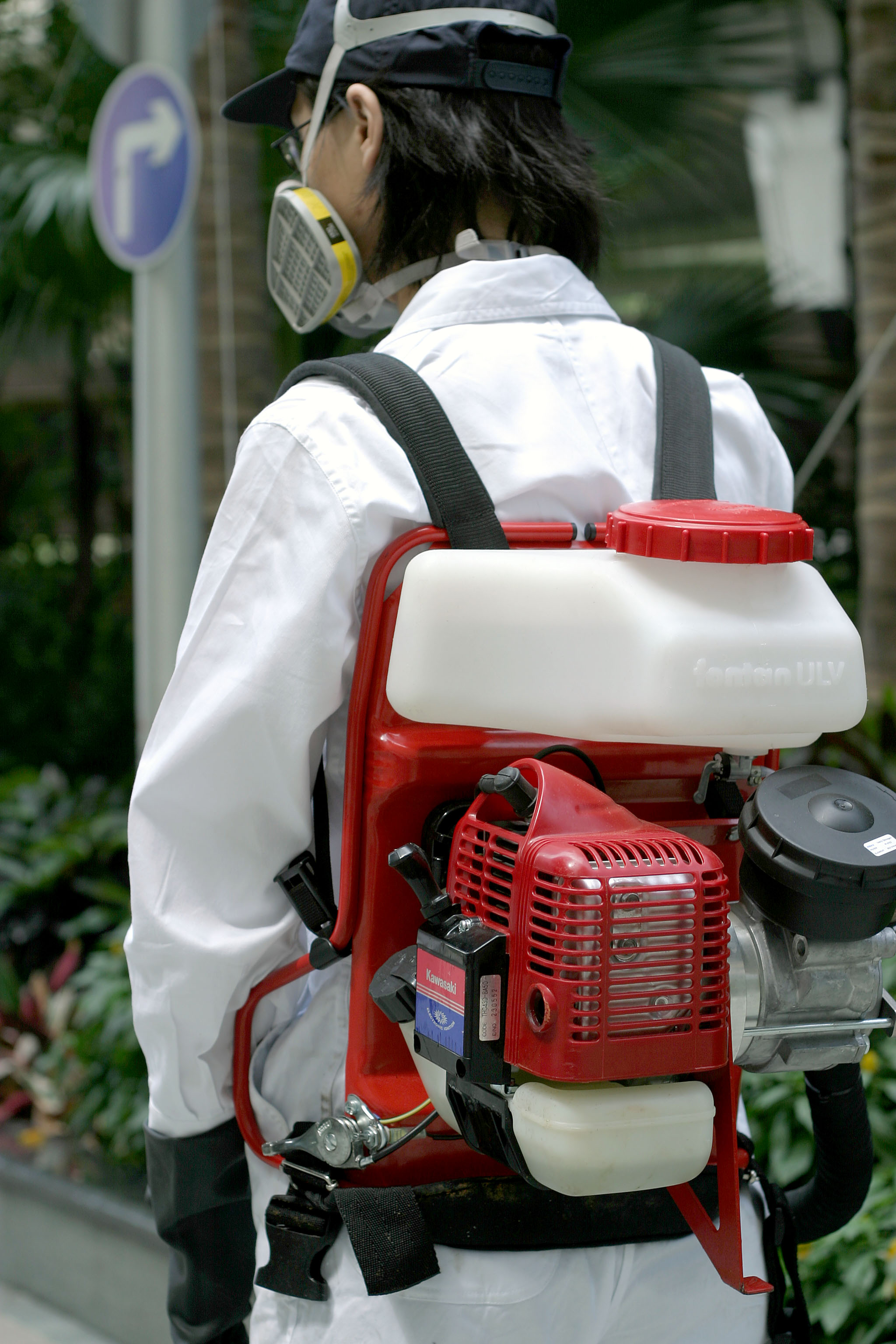

Mosquitoes
HOME > PEST CONTROL SOLUTION > MOSQUITOES
Problems
- Mosquitoes can act as vectors for many diseases such as Malaria, Dengue Fever and Japanese Encephalitis.
- Only female mosquitoes feed on blood. When a human is bitten, the immune system will respond to the antigens in a mosquito’s saliva. Reactions to the bite include itchiness, redness of the skill and swelling.
Common Source
- Mosquitos grow from eggs into Larva, then Pupa, and finally into an adult. They breed rapidly and a female can lay 100 to 200 eggs over a lifetime of only one to two weeks.
- Mosquitos are usually found in ponds, ditches or any containers that hold water, such as the plate under a flower pot. Mosquitoes breed in these places and develop into adults.
Prevention / Solutions
- Thoroughly check and detect the presence of termites by using professional equipment as well as identifying any potential harbourages for termites.
- Selected drilling of holes to apply a termiticide; an appropriate termiticide will eliminate termites, provide a barrier to prevent termite expansion, and destroy termites’ nests.
- Nixon uses professional termite monitoring and trapping technologies including underground or in-wall devices and outdoor traps. These tools can eliminate termites from their nest. This kind of eco-agent bait is safe and effective. The bait and pesticide will only be effective to termites, but is not harmful to humans unless a large amount is intentionally ingested.
Prevention / Solutions
- Store food carefully. Ensure that no food is left exposed on benches, tables, floors, etc.
- Eliminate access points by filling in any cracks in walls, floors, etc. as well as covering drains with wire mesh to prevent cockroaches entering your dwelling.
- Reduce as much as practical unnecessary furniture, fixtures, etc.
- Apply an appropriate insecticide; spray the skirting of walls, door frames, drainage and any other area where cockroaches could dwell.
- Applying cockroach baits to strategic locations such as cabinets, door joints and electric sockets.
- Use an ultra low volume (ULV) spray for ceilings and walls.
Prevention / Solutions
- Keep beds, cabinets and wooden furniture clean.
- Ensure your pet is kept clean, hygienic and healthy。
- Launder clothes as soon as possible when returning from the outdoors; if possible, launder clothes at a high temperature for better hygiene.
- Spray pesticide on the skirting of walls and any wooden parts of furniture.
- A single treatment may not be effective; a well-designed schedule of treatments is required for complete termination of fleas
Prevention / Solutions
- Inspection and location of bees and beehives.
- Wearing protective clothing and spraying of pesticides.
- Physically removing beehives.
Prevention / Solutions
- Thermal fog treatment
The application of pesticides using a thermal fogger allows for greater coverage and more effective penetration of mosquito harbourages. Mosquitoes and other flying insects will die once they make contact with pesticides. Due to the production of smoke in the fogging process, it is not recommended to use this application in densely populated areas or confined spaces. - ULV treatment
A low volume application of pesticides will also effectively kill mosquitoes upon contact. It is not recommended to use ULV treatment in densely planted areas. - Elimination of Larvae
Placing larvicidal oil or larvicidal sand in harbourages where mosquito larva are likely to habitat can ensure elimination of larvae before they grow into Pupa and then mosquitos.
Larvicidal oil is a mineral oil. By applying a thin layer of oil on water, the larva suffocates due to the lack of oxygen in the water. As larvicidal oil is decomposed by microorganisms and sunlight, the appropriate dosage will not affect aquatic life or otherwise damage the eco-system. - Regular checking for and elimination of any potential harbourages, particularly stagnant water, where mosquitos thrive.
Prevention / Solutions
- Ensure food is carefully stored and preserved and. Also, make sure no food is left on the ground or other surfaces.
- Fill gaps and niches in walls or on the ground to prevent access by ants or other pests.
- Application of insecticide by spraying on skirtings, doors, windows and drainage.
- Using baits inside cabinets and near electrical sockets.
- Using ULV spraying on ceilings and walls.
Prevention / Solutions
- Good hygiene is a vital factor in the control of rats. Store and preserve food carefully to avoid been targeted by rats.
- Maintain good hygiene and handle and dispose of food waste properly.
- Using food as a bait to identify a rat’s location.
- Eliminate sources of food for rats.
- Place rodenticides in areas where rodents are known to frequent and undertake regular inspections.